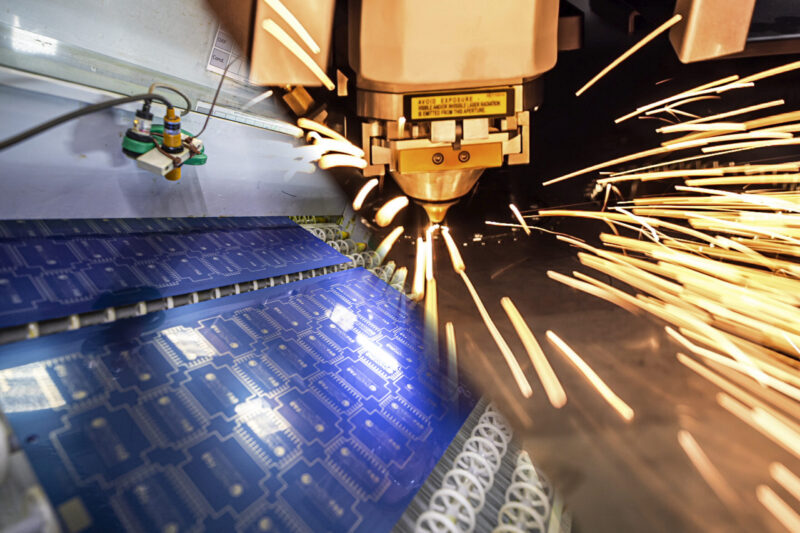
Batteries and chemical etching
The future of battery manufacturing in the UK.
In a fossil-fuel-less world, the demand for high-performance batteries will continue to multiply. This will cause huge-scale waves in technology innovation for the battery manufacturing industry.
There are factors holding the UK back from positioning itself as a global powerhouse in battery manufacturing. From electricity prices to investment, the UK has to break down these barriers to create a fruitful battery industry.
Here, we explore the importance of developing a battery industry in the UK and how chemical etching could hold the key.
Why does battery manufacturing matter for the UK?
Firstly, why should the UK even care about becoming a global leader in battery production?
It’s hard to overlook the economic importance of creating a top-five battery manufacturing industry. A thriving battery industry could pave the way for an industrial renaissance in the UK, creating highly skilled jobs, not only in the production but in research and development and engineering.
The potential for attracting governmental funding and investment, and that from external sources, is a given in a strong battery production industry.
Having a strong position within domestic battery production can help to stimulate growth within other key industries that are developed from within the UK. For native manufacturers, having a battery manufacturer on their doorstep can help to speed up supply chains and make trading easier without a demand on foreign imports.
Creating a high quality battery manufacturing industry can help the UK’s net zero goals with an increased likelihood of transport electrification or the storage of renewable energy in batteries for, say, microgrids.
Global perception of being a technological leader is only a positive thing.
So, what’s stopping the UK from becoming leaders?
Well, much of the typical raw material needed for battery production comes from overseas – think lithium, cobalt and nickel. This can cause supply chain issues and price volatility and requires investment into refinding and processing facilities.
Europe’s highest industrial energy costs can make the cost of battery production less competitive. In a highly competitive industry, with some key players already established, this could be key to selling or not.
The UK’s strong research capabilities and supportive government initiatives, such as the Faraday Battery Challenge, offer opportunities for growth. By addressing supply chain vulnerabilities, reducing energy costs, and investing in talent development, the UK can position itself as a major player in the global battery market.
Using innovative technologies and manufacturing processes, using alternative engineering processes can help the UK to differentiate itself from the battery competition.
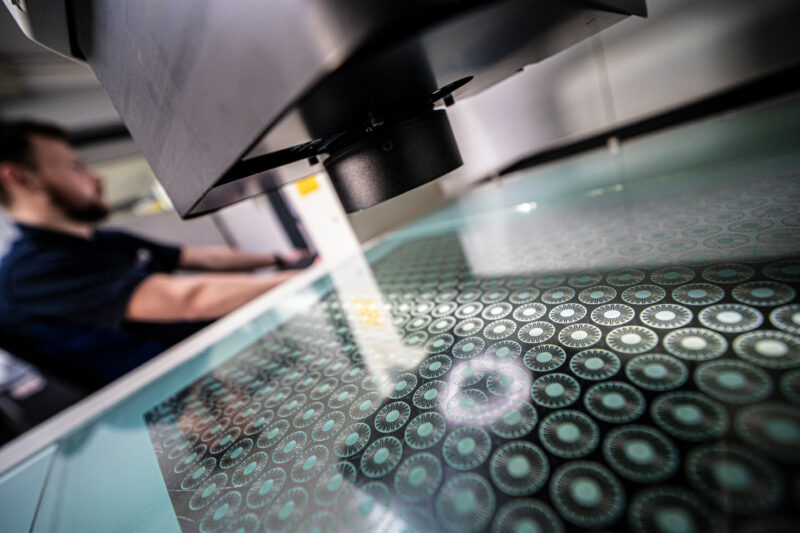
How chemical etching can revolutionise battery production
Traditional battery manufacturing processes should be challenged and design engineers should be open to taking each and every opportunity to produce higher quality products.
The future of battery manufacturing is intricately linked with the evolution of chemical etching technologies. As research continues to advance, the potential for even more refined and efficient battery components becomes increasingly attainable.
Ongoing research is exploring the use of chemical etching in conjunction with other innovative technologies, such as nanostructuring and three-dimensional printing, to create next-generation battery architectures. These advancements promise to deliver batteries with unprecedented energy densities and longevity.
For chemical etching to achieve its full potential in battery manufacturing, collaboration across the industry is essential. Partnerships between research institutions, manufacturers, and technology developers can accelerate the development and integration of this technology, paving the way for revolutionary advancements in energy storage.
Enhancing battery efficiency, reducing production costs, and fostering sustainable practices, chemical etching can revolutionise how batteries are designed and manufactured. That’s how to advance the industry.